- Home >
- Learning centre >
- Science blog >
- Advancing Microbial Studies: Biocalorimetry Sheds Light on Surface-Bacteria Interactions
Advancing Microbial Studies: Biocalorimetry Sheds Light on Surface-Bacteria Interactions
30th January 2026
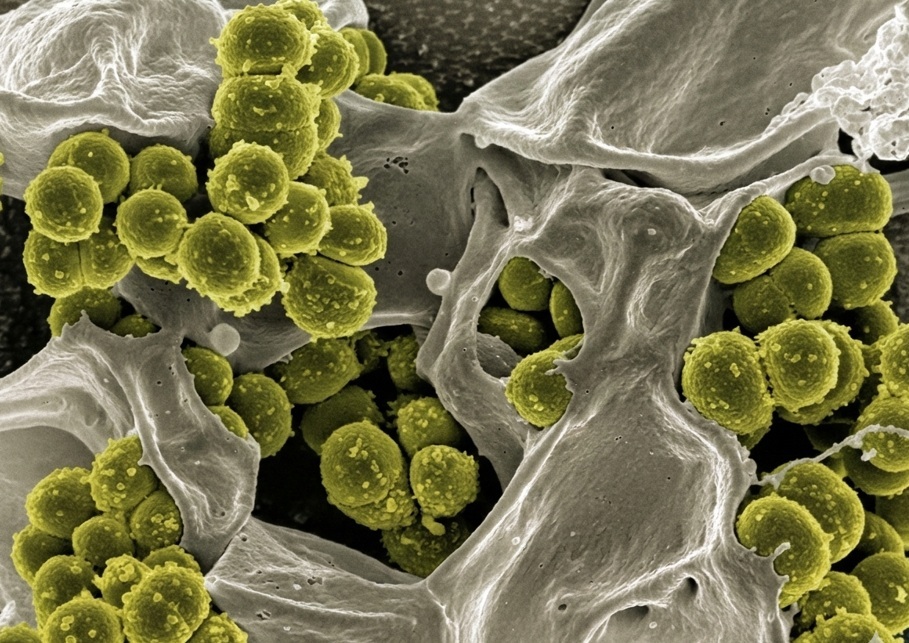
The Challenge of Measuring Microbial Interactions on Uneven Surfaces
Understanding the interactions between bacteria and complex material surfaces remains a challenge in microbiological research. Conventional techniques often fall short in providing real-time, quantitative insights, particularly on intricate surfaces such as orthopedic implants. In a 2025 publication in Antibiotics, Harald Holeczek, Michael de Wild, Jasmine Ruegg, Philipp Gruner, Walter Moser, and Olivier Braissant demonstrated how biocalorimetry based on isothermal microcalorimetry (IMC) can be used to investigate these interactions in significantly greater detail.
Revealing Microbial Behavior on Orthopedic Implants Using Isothermal Microcalorimetry
Orthopedic implants are designed with intricate geometries to enhance integration with the human body. However, these designs also create microenvironments, grooves, crevices, and rough surfaces, that are prone to microbial colonization. Bacteria that inhabit these microstructures can form biofilms, which pose significant risks of infection and implant failure. Traditional methods to study these processes, such as endpoint assays, are limited in their ability to capture the dynamic and spatially localized interactions between bacteria and these materials.
Biocalorimetry provides a solution to these challenges by offering real-time, continuous measurements of metabolic heat production. §This allows researchers to monitor bacterial activity and growth directly on material surfaces. In the study, Holeczek and colleagues applied IMC to evaluate the antimicrobial properties of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂)-coated titanium, a potential coating for orthopedic implants. The coating showed significant inhibitory effects on Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus, two bacteria commonly associated with implant-related infections.
The study found that the Ca(OH)₂ coating extended the lag phase and reduced the growth rate of bacteria in a manner that was dependent on inoculum density. These findings demonstrate the ability of biocalorimetry to reveal nuanced microbial responses that conventional methods might miss.
insights into Microbial Interactions on Complex Surfaces
One of the unique strengths of biocalorimetry is its ability to measure bacterial activity on non-flat and porous surfaces, such as the screws used in this study. By simulating in vivo-like conditions, biocalorimetry provided valuable insights into how the alkaline environment created by the Ca(OH)₂ coating affected bacterial metabolism. This approach revealed localized antimicrobial effects at the material surface, emphasizing the importance of studying interactions in situ.
The study also highlighted the potential for the Ca(OH)₂ coating to hydrolyze endotoxins, which are implicated in aseptic loosening of implants. This dual functionality—antimicrobial activity and endotoxin neutralization—positions the coating as a promising solution for improving implant safety and longevity.
The findings of this study are particularly relevant for the development of next-generation orthopedic implants. The ability to quantitatively assess bacterial behavior on complex surfaces provides a pathway for optimizing antimicrobial coatings and understanding their performance under clinically relevant conditions. Beyond orthopedics, the principles demonstrated here could be applied to other biomedical devices, such as dental implants and surgical tools, where microbial colonization poses significant risks.
Learn more
Read more about biofilm testing with calScreener biocalorimeter and clinical research using biocalorimetry.

STAY UP-TO-DATE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay up to date with the latest news and updates